MOTHERBOARD
What is a motherboard?
The motherboard is the main board of a computer. It is the connection and communication hub between all components: processor (CPU), RAM memory, storage, graphics card, and more. Without it, nothing works.
Main functions
-
Interconnection: connects all the PC components.
-
Power distribution: receives power from the power supply and distributes it.
-
Control and management: contains the firmware (BIOS/UEFI) and chipsets that manage the hardware.
-
Physical support: allows mounting components such as RAM, CPU, GPU, hard drives, etc.
-
Expansion: offers slots for additional cards.
-
Connectivity: provides USB ports, network, audio, video, etc.
Main components of a motherboard
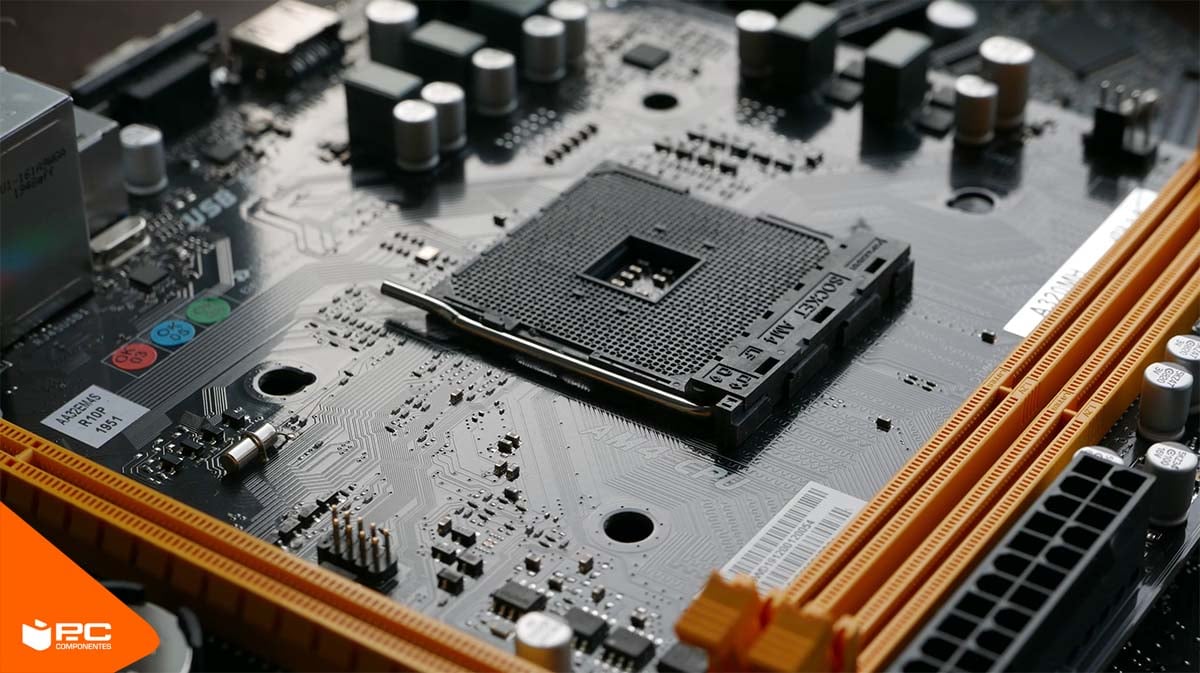
CPU socket
-
The place where the processor is installed.
-
Examples: LGA 1700 (Intel), AM5 (AMD).
-
Must be compatible with the CPU you want to use.
Chipset
-
The “secondary brain” that determines which functions and ports are available (USB, PCIe, etc.).
-
Example: Intel Z790, AMD B650.
RAM slots (DIMM)
-
Slots where the memory goes.
-
Types: DDR4 or DDR5 (they are not compatible with each other).
-
Supports certain speeds and capacities depending on the model.
PCIe slots
-
Slots to connect graphics cards (GPU), sound cards, network cards, etc.
-
Versions: PCIe 3.0, 4.0, 5.0 (higher number = higher speed).
Storage ports
-
SATA: for hard drives (HDD) and 2.5" SSDs.
-
M.2: for NVMe or SATA SSDs, much faster and more compact.
Form factors (board sizes)
-
ATX: standard, larger, more ports.
-
Micro-ATX (mATX): smaller, fewer ports.
-
Mini-ITX: very compact, ideal for small PCs.
Key compatibility factors when choosing a motherboard
-
Socket: must be compatible with your processor.
-
RAM type: DDR4 or DDR5, maximum supported capacity and speed.
-
Form factor: must fit inside your case (chassis).
-
Chipset: defines available features and ports.
-
Storage: number of M.2 slots and SATA ports.

No comments:
Post a Comment